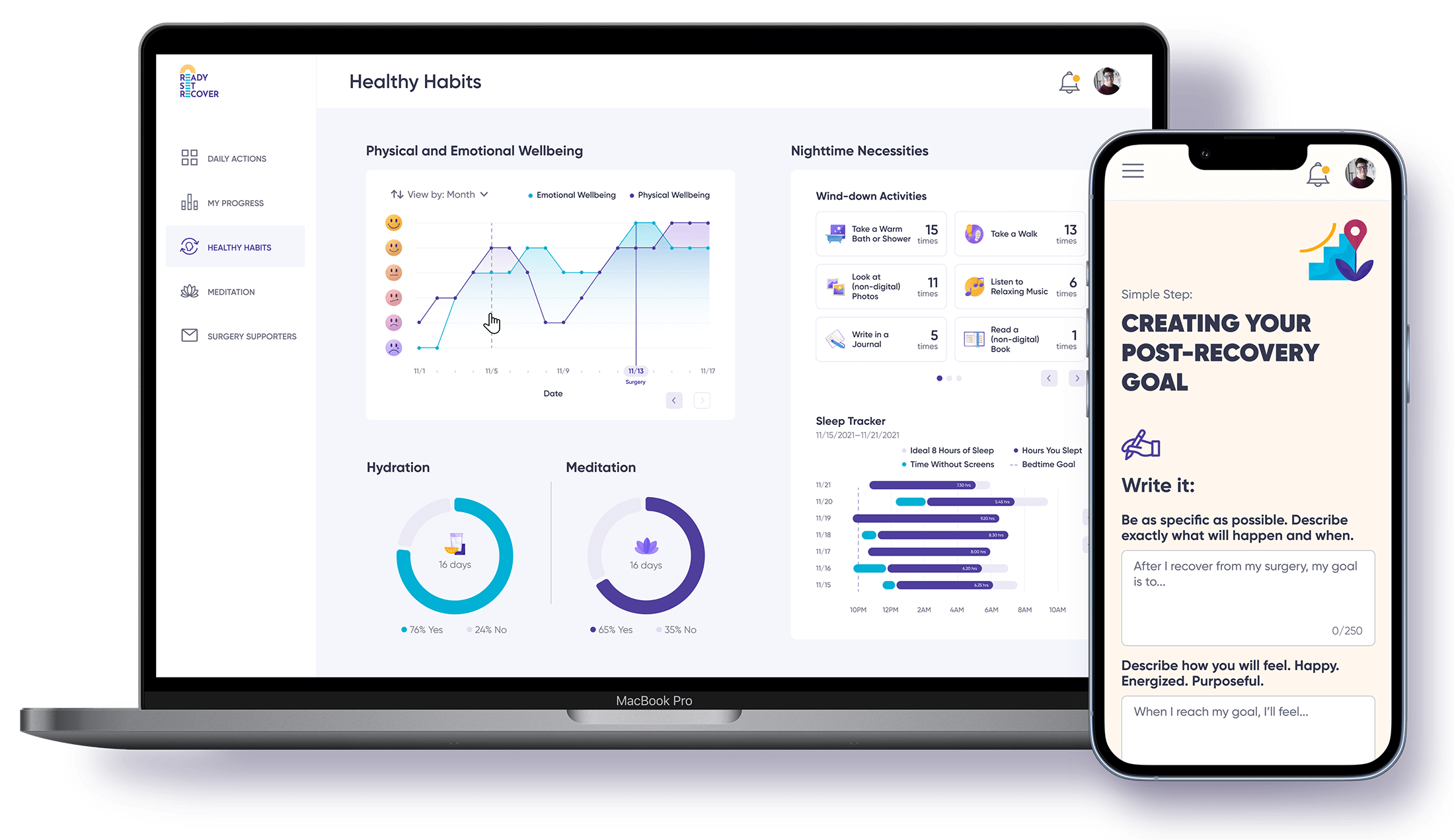
How AI and Medical Diagnosis Are Changing Healthcare


Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of healthcare, with particularly significant implications for medical diagnosis. This article explores the pivotal role AI is playing in revolutionizing diagnostic processes across the medical field.
Key Takeaways
AI technologies are transforming healthcare by enabling more accurate and faster disease diagnosis, analyzing medical images, and processing large datasets to detect patterns often missed by human practitioners.
The integration of AI in healthcare focuses on augmenting rather than replacing human intelligence, providing advanced tools to healthcare professionals for better patient outcomes, more effective treatment plans, and improved diagnostic precision.
AI applications in medical diagnostics, such as imaging diagnostics, genomic medicine, and blood tests, have shown significant promise in early disease detection, personalized treatment plans, and reducing diagnostic errors, despite challenges related to data privacy, bias, and regulatory standards.
How AI and Medical Diagnosis Work Together
Introduction
AI and medical diagnosis are transforming the way doctors detect and treat illnesses. By scanning medical records, lab tests, and images, AI identifies patterns that the human eye might miss. AI also enhances decision-making. With real-time data, doctors can compare patient symptoms to thousands of past cases, leading to more accurate diagnoses. This means fewer misdiagnoses, faster treatment plans, and better patient outcomes.
Understanding AI in Medical Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnosis refers to the use of computer systems to perform tasks that require human intelligence, such as learning, pattern recognition, and decision-making. The core technologies driving AI in healthcare include machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. These technologies enable AI algorithms to analyze patient data, identify patterns, and assist in the diagnostic process.
Machine learning, a subset of AI, involves training algorithms on large datasets to recognize patterns and make predictions. Think of it like teaching a computer to spot trends, just like how we learn from experience. Deep learning, a more advanced form of machine learning, uses neural networks with multiple layers to process complex data and extract meaningful insights. Imagine it as a super-smart brain that gets better at understanding things the more it practices. Natural language processing allows AI systems to understand and interpret human language, making it possible to analyze unstructured medical data such as doctor’s notes and electronic health records. It's like giving computers the ability to read and understand our language, so they can help make sense of all the written information in healthcare.
AI’s ability to analyze multimodal medical data, including medical images, genetic information, and patient history, enhances the diagnostic process and improves clinical diagnosis. By leveraging AI, healthcare providers can achieve more accurate diagnoses, reduce costs, and save time while minimizing human errors. AI’s potential to revolutionize personalized medicine, optimize medication dosages, and enhance population health management is immense.
Even though AI possesses transformative potential, its effectiveness in medical diagnostics is maximized when combined with the expertise of healthcare professionals, including medical professionals. Physicians play a critical role in interpreting AI-generated insights and making informed clinical decisions. This collaboration between AI technology and human intelligence can lead to better patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.
Key Applications of AI in Medical Diagnosis
AI offers a variety of promising applications in medical diagnosis. Three key areas where AI has made significant strides include imaging diagnostics, genomic medicine, and blood tests and biomarkers. Each of these applications leverages AI’s ability to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and provide accurate and timely diagnoses.
AI in Imaging Diagnostics

AI has revolutionized imaging diagnostics by enhancing the analysis and interpretation of medical images such as:
X-rays
MRIs
Ultrasounds
CT scans
AI algorithms, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are instrumental in interpreting these images, leading to more accurate and faster diagnoses. By identifying patterns that may be missed by human radiologists, AI tools can provide early detection of diseases. Essentially, CNNs act like super-smart eyes that can scan and understand medical images with incredible precision. They can spot tiny details and anomalies that even the best human radiologist might overlook. This means that diseases can be caught earlier, which is crucial for effective treatment. Imagine having a highly skilled assistant who never gets tired and can look at images all day without missing a beat – that's what AI brings to medical imaging.
One notable application is AI’s ability to analyze MRI scans and highlight regions of interest that may require further investigation. This not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also accelerates the diagnostic process, allowing for quicker patient diagnoses. AI-powered medical imaging technology helps doctors identify abnormalities and detect diseases with greater precision and speed.
AI-based medical imaging has also been used to provide quantitative evaluations of radiographic traits and identify complex patterns in imaging data. These advancements have led to the development of innovative tools and techniques that can assist radiologists in their daily tasks. For instance, AI can help in segmenting organs and tissues in medical images, which is crucial for planning surgeries and other medical procedures. Additionally, AI systems are being trained to detect minute changes in imaging data over time, allowing for the monitoring of disease progression and the effectiveness of treatments. This continuous monitoring can lead to more timely interventions and better patient outcomes.
Moreover, AI-powered imaging tools are being integrated into telemedicine platforms, enabling remote diagnostics and consultations. This is particularly beneficial in rural or underserved areas where access to specialized medical care is limited. By providing accurate and timely diagnostic information, AI in medical imaging is helping to bridge the gap in healthcare accessibility and ensure that patients receive the care they need, regardless of their location. These advancements in AI imaging diagnostics are paving the way for more accurate and effective disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
AI in Genomic Medicine

AI’s role in genomic medicine is transformative, enabling the analysis of genetic data to assess disease risk and develop targeted treatments. Machine learning algorithms can analyze large genomic datasets to discover new genetic markers for various conditions. This capability allows healthcare professionals to identify genetic mutations associated with diseases, enhancing risk assessment and diagnosis.
AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets extends to drug discovery, where it can identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy. This contributes to the development of personalized treatment plans that are tailored to an individual’s genetic profile. By leveraging AI, medical practitioners can provide more precise and effective interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
The integration of AI in genomic medicine holds great promise for the future of personalized healthcare. As AI technologies continue to advance, they will play a crucial role in identifying genetic risk factors, developing targeted therapies, and improving overall patient care.
AI in Blood Tests and Biomarkers

AI systems are enhancing the analysis of blood tests by identifying patterns and biomarkers indicative of early disease stages. This capability is crucial for timely intervention and better patient outcomes. Using AI algorithms to analyze blood biomarkers improves the accuracy of disease detection and monitoring, particularly for chronic diseases.
AI's role in blood tests extends beyond merely identifying patterns; it also involves the integration of various data sources to provide a comprehensive view of a patient's health. By combining blood test results with other medical data such as genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle factors, AI can offer more precise and personalized health assessments. This holistic approach enables healthcare providers to detect diseases at their earliest stages, often before symptoms appear, allowing for proactive management and treatment.
Moreover, AI-driven blood test analysis can facilitate the discovery of novel biomarkers that were previously undetectable using traditional methods. These new biomarkers can lead to the development of innovative diagnostic tests and therapies, further advancing the field of personalized medicine. AI's continuous learning capabilities also mean that as more data is collected, the algorithms become increasingly accurate, improving their predictive power over time.
In addition to chronic disease management, AI-enhanced blood tests are proving invaluable in areas such as oncology, where early detection of cancer biomarkers can significantly improve patient prognosis. By identifying specific biomarkers associated with different types of cancer, AI can help oncologists tailor treatment plans to the individual needs of each patient, optimizing outcomes and reducing the likelihood of adverse effects.
Overall, the integration of AI in blood test analysis represents a significant leap forward in medical diagnostics, offering the potential for earlier detection, more accurate diagnoses, and personalized treatment plans that improve patient care and outcomes.
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy with AI

The ability of AI to process vast medical data and recognize patterns unseen by human clinicians, is transforming diagnostic accuracy. By leveraging AI tools, healthcare providers can surpass human performance in disease diagnosis, treatment selection, and clinical laboratory testing, leading to better patient outcomes.
Reducing False Positives and Negatives
Deep learning algorithms, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), play a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy by reducing human error and oversight. These algorithms can accelerate the analysis of medical tests, providing quicker and more accurate predictions. For instance, AI-based tools like CNN-LSTM architectures have been shown to enhance the efficiency of diagnostic processes by minimizing false readings.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are another example of deep learning models that can significantly reduce false positives and negatives in medical diagnostics. Simply put, GANs help in ensuring that the diagnosis is more accurate by minimizing the chances of mistakes, leading to better patient outcomes and more reliable diagnoses.
Long short-term memory (LSTM) algorithms are smart assistants that help doctors by remembering important details over time. They look at medical data carefully to avoid mistakes, making sure the diagnosis is as accurate as possible. This means fewer errors and better care for patients. LSTM networks are particularly adept at handling sequential data, making them invaluable in analyzing time-series data from patient records, such as monitoring vital signs or tracking the progression of chronic conditions. By maintaining and updating a 'memory' of past data points, LSTMs can provide insights that help in predicting future health events, thus enabling proactive medical interventions. This advanced capability ensures that healthcare providers can make well-informed decisions, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized patient care.
Integrating AI into Clinical Practice
Integrating AI into routine clinical practice presents both challenges and opportunities. AI has the potential to enhance patient care across healthcare settings by diagnosing diseases, developing personalized treatment plans, and assisting clinicians with decision-making. However, successful adoption requires careful validation, training, and ongoing monitoring to ensure accuracy, safety, and effectiveness.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Introducing AI in healthcare involves numerous ethical and legal considerations, including aspects like data privacy, informed consent, patient autonomy, and countering bias in AI systems.
Health care professionals, as healthcare providers, must navigate these complexities to ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically in patient care.
Learn more about the pros and cons of using AI for medical advice.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security are paramount in AI healthcare applications. Procedures such as de-identification and anonymization of patient data are critical to protecting patient information in AI systems. Healthcare providers must also implement strong encryption methods to secure patient information during storage and transmission, safeguarding against potential cyberattacks.
Significant risks are associated with compromised patient data, which can cause disruption in healthcare operations and endanger patient safety. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe is essential for protecting patient privacy. Third-party vendors handling patient data must adhere to these regulations to maintain high standards of data protection.
Improving transparency in AI algorithms and ensuring patient data privacy are ongoing research areas. Stakeholders must collaborate to create standards for AI security and address issues related to data interoperability, ensuring that AI healthcare applications are both secure and effective.
Addressing Bias in AI Systems
Bias in AI systems presents a major concern, given that it can foster healthcare disparities across diverse demographic groups. The availability of representative datasets is essential to prevent bias in AI healthcare applications. Incomplete or biased training datasets can lead to skewed outcomes, negatively impacting patient care.
Ensuring fairness in AI healthcare applications involves:
Rigorous testing and validation of algorithms to identify and mitigate biases. For example, conducting extensive trials across diverse patient populations to ensure the AI performs equally well for different demographic groups.
Addressing ethical concerns, including cognitive or algorithmic bias. This might involve setting up ethics committees to review AI systems and ensure they adhere to ethical standards.
Creating equitable and effective AI-driven healthcare solutions. For instance, developing AI tools that are specifically designed to improve healthcare access in underserved communities or regions.
Collaboration between healthcare providers, AI developers, and regulatory bodies is essential to address bias and ensure that AI applications promote health equity. Ongoing efforts to improve data quality and representativeness will help mitigate biases and enhance the reliability of AI systems in healthcare.
Challenges and Future Directions
The implementation of AI in healthcare comes with its own set of challenges. Issues such as data quality and availability, regulatory barriers, and the need for collaboration between stakeholders must be addressed to fully realize AI’s potential in healthcare.
Future research opportunities in AI for healthcare include developing more robust methods to manage biases and improve data quality.
Data Quality and Availability
High-quality labeled data is crucial for training accurate AI models in healthcare. However, data collection is often incomplete and localized, hindering AI performance and limiting its effectiveness.
The lack of standardized protocols for data collection and management also poses a significant challenge for AI adoption. Efforts to improve data quality and availability must focus on:
Creating comprehensive and standardized datasets
Training AI models effectively
Enhancing diagnostic accuracy
Providing reliable and trustworthy insights
Healthcare professionals, researchers, and tech developers need to join forces to create strong data management systems. By collaborating, they can build frameworks that ensure AI in healthcare is accurate and effective.
Collaboration Between Stakeholders
Successful adoption of AI in healthcare necessitates continuous collaboration among healthcare providers, AI developers, and regulatory bodies. Organizations like the Health AI Partnership are working to establish best practices for responsible AI deployment in healthcare. These collaborations are crucial for addressing the ethical, legal, and technical challenges associated with AI in healthcare.
Healthcare organizations, AI researchers, and medical specialists must work together to ensure that AI applications meet the highest standards of accuracy, safety, and effectiveness. By fostering a collaborative environment, stakeholders can share knowledge, resources, and expertise to develop AI solutions that benefit patients and healthcare providers alike.
Establishing clear guidelines and best practices for AI deployment in healthcare will help build trust and confidence in AI technologies. Continuous dialogue and cooperation between stakeholders will ensure that AI-driven healthcare applications are implemented in a manner that promotes patient safety and improves health outcomes.
Will AI and Medical Diagnosis Replace Doctors?
AI is undeniably a game-changer in the healthcare industry, but we are still in the early days of its integration. While some applications, such as imaging diagnostics and personalized treatment plans, are already showing promise, it may take time for these technologies to become effective or implemented at scale. The potential for AI to revolutionize healthcare is tremendous, with many applications yet to be conceived.
Historically, many groundbreaking technologies have evolved significantly from their initial discovery. Take the example of the X-ray. When Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays in 1895, it was a revolutionary breakthrough. However, it took decades for the technology to be refined and widely adopted in medical diagnostics. Similarly, the invention of the MRI in the 1970s has since evolved into a critical tool for non-invasive medical imaging, transforming how we diagnose and treat various conditions.
Another example is the development of antibiotics. When Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1928, it marked the beginning of a new era in medicine. However, it wasn't until the 1940s that antibiotics were mass-produced and became widely available, saving countless lives and changing the course of medical treatment.
AI in healthcare is following a similar trajectory. While we can already see its transformative potential, many applications will require further research, development, and integration into existing healthcare systems. As AI continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly uncover new possibilities and applications that we can't even imagine today.
It's an exciting time to be in the healthcare industry, as AI promises to bring quantum leaps in medical advancements. Whether it's through early disease detection, personalized medicine, or improved patient care, the future of healthcare looks brighter with AI leading the way. Whatever happens, the advancements brought by AI will represent monumental leaps from the present-day state of medicine, ushering in a new era of healthcare excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI's role in improving diagnostic accuracy in healthcare?
AI plays a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy by analyzing large amounts of medical data, identifying patterns, and providing accurate and timely diagnoses, surpassing human performance in disease diagnosis and treatment selection.
How does AI contribute to personalized treatment plans?
AI contributes to personalized treatment plans by analyzing patient-specific data and genetic information, allowing for the creation of tailored treatment plans that improve the effectiveness of medical interventions and promote better patient outcomes.
What ethical concerns are associated with AI in healthcare?
Healthcare providers must ensure that AI is used responsibly and ethically in patient care, addressing concerns such as data privacy, informed consent, patient autonomy, and bias in AI systems.
What are the main challenges in implementing AI in healthcare?
The main challenges in implementing AI in healthcare are data quality and availability, regulatory barriers, and the need for collaboration between stakeholders. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for the successful integration of AI in healthcare.
How can stakeholders collaborate to ensure effective AI adoption in healthcare?
Stakeholders in healthcare can collaborate by creating robust data management frameworks, establishing clear guidelines and best practices, and fostering continuous dialogue and cooperation to ensure the effective adoption of AI. The Health AI Partnership is an example of an organization that promotes responsible AI deployment in healthcare.
Can AI diagnose my symptoms?
AI tools can suggest possible conditions based on your symptoms, but they aren’t a replacement for a doctor. They provide guidance, not a definitive diagnosis, so it’s always best to consult a medical professional.